

人體的染色體及基因分別遺傳自父母,孩子不但會遺傳到父母的身體及外貌特徵,包括眼睛、血型等;有些更會遺傳雙親的天賦才藝,在特定領域有傑出的成就。
如果父母遺傳給下一代的並不是天賦外貌,竟然是不幸的隱性致病基因,為什麼從來不知道呢?
很多時隱性遺傳病基因攜帶者是健康及無明顯症狀,也沒有家族遺傳病史,即使致病基因雖然會代代相傳,但並非每個家族都會出現患者。因此,大部份隱性遺傳病基因攜帶者都不知道自己帶有致病的突變基因。如果父母雙方都帶有的隱性致病基因,下一代就有機會是重症患者。
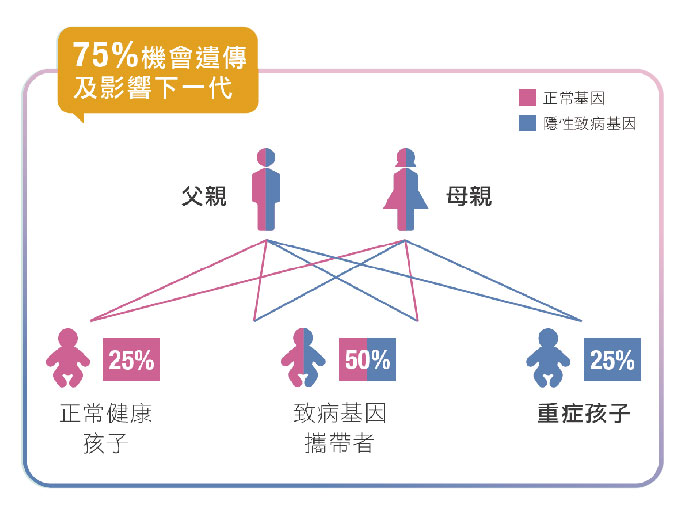
研究顯示,平均每1個人就帶有2.8個帶有隱性致病基因。如果父母都有隱性致病基因,有3/4機會將相關基因遺傳給下一代,孩子有1/4機會是重症患者,嚴重更會終身畸形、殘障及死亡。
常見遺傳病如地中海貧血,患者或需終生輸血、死亡率高;嚴重遺傳病如多囊腎病,患者中年時期才發病且無藥可醫,只可靠洗腎延緩惡化;晚發型龐貝氏症初期症狀與其它神經肌肉疾病症狀相似,33%病患曾被誤診為其他疾病,導致延誤治療時機。因此,若能夠盡早知道下一代患上隱性遺傳病的風險,就可以幫助計劃生育的夫婦及於懷孕初期的孕婦預先作準備。
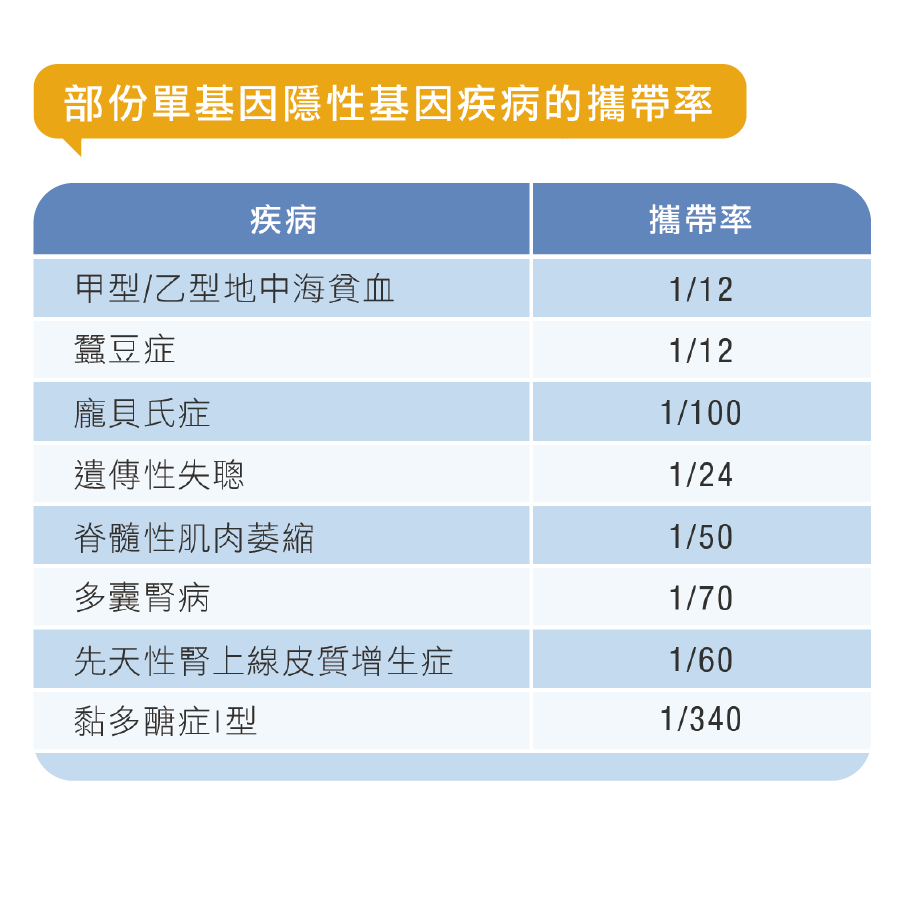

HeredScreen基康檢隱性遺傳病基因檢測可讓夫婦及早發現隱性致病基因,如發現二人均有相同的疾病基因,早期懷孕的孕婦可得知寶寶日後會否有健康及發育問題。夫婦可盡早於懷孕時、寶寶出生後、日後成長方面,規劃好所需的支援。
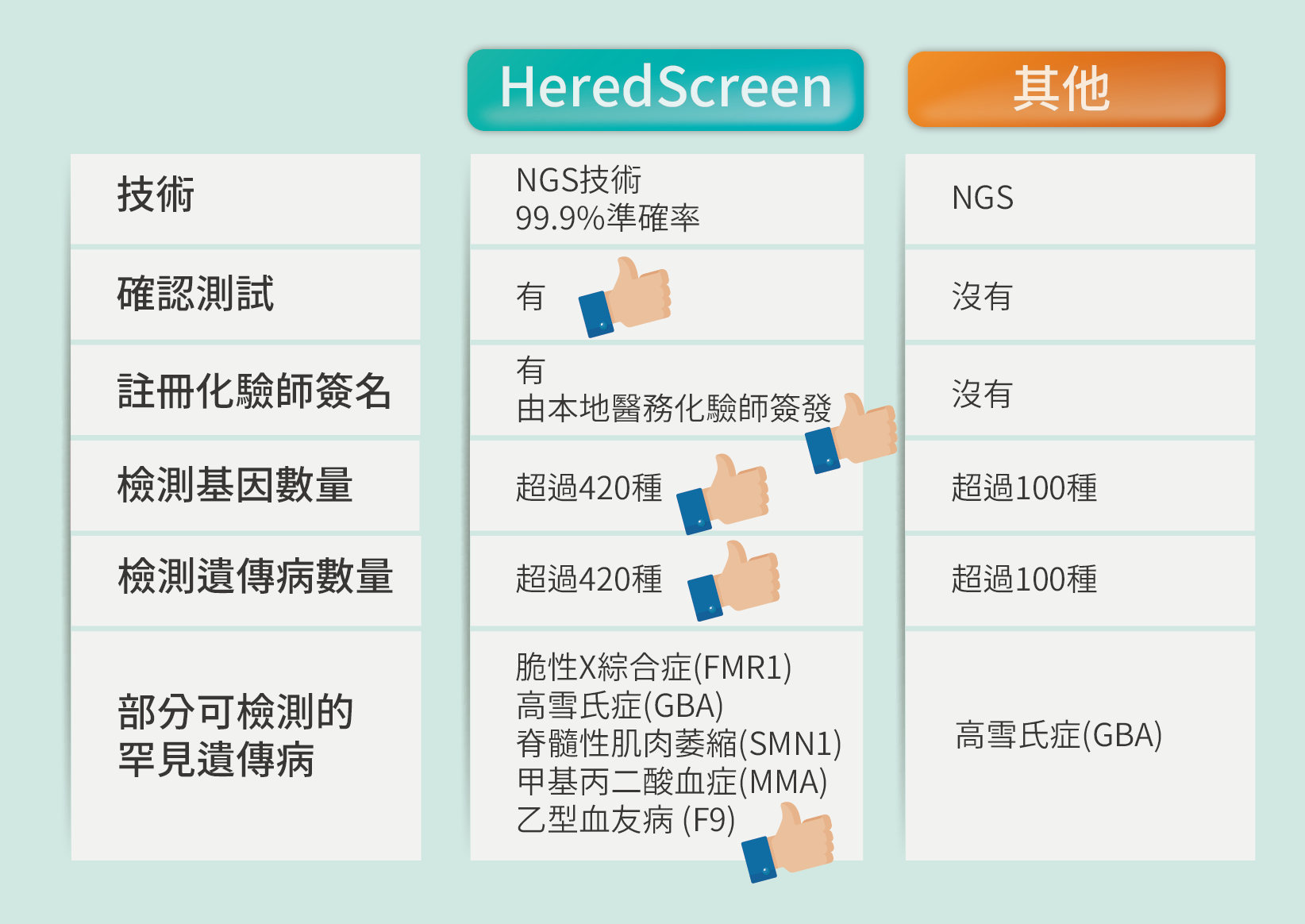
⦁ 全面涵蓋300+種隱性基因疾病,覆蓋香港最常見的隱性遺傳病
⦁ 採用次世代測序技術(NGS)超大規模測序,一次過檢查數以百萬計基因段,每個位置檢查最少50次
⦁ 準確率高達 99.9%
⦁ 有效分辨脊髓性肌肉萎縮症的沉默基因攜帶者
⦁ 採用最新測序技術「固態測序」,將整條FMR1基因讀取,一次性檢測就能精確評估脆性X綜合症風險
⦁ 詳細報告列明風險疾病資訊、基因狀況及疾病風險等
| 適用對象 | |||
| 進行婚前檢查伴侶 | 計劃懷孕夫婦 | 早期懷孕階段孕婦 | 進行人工受孕夫婦 |
| 測試代碼 | 測試名稱 | 樣本要求 | 測試需時 (工作天) | 檢測費用 |
| HERED | 420+隱性基因疾病檢測 | 6mL EDTA採血管 x 1 | 30 |
$7,900
|


完成測試後,有機會獲免費骨質密度檢查 (DEXA) 乙次 或 骨質密度檢查優惠券乙張
閣下資料將會用作此推廣活動聯絡用途,如因資料有誤而未能聯絡閣下,本公司一概不負上任何責任。