07.30.2018
Pneumococcal 13-Valent Vaccine

Pneumococcus
Features
Streptococcus pneumoniae (or pneumococcus) infections are referred to as pneumococcal infections. Although pneumococcus is most commonly associated with sinusitis and otitis media, it causes serious and fatal invasive pneumococcal illnesses such as pneumonia, septicemia, and meningitis. In young children and the elderly, the consequences of invasive pneumococcal illness are frequently severe.
Pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under the age of 5.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 1 million children under the age of 5 die each year from pneumococcal illness worldwide. Antibiotic resistance in pneumococcus treatment used to be as high as 100%. Once infected, it will increase the difficulty of treatment, delay the disease, and even make the treatment ineffective.
Vaccination, according to the organization, is the most effective strategy to avoid drug resistance and infectious diseases.
Mode of transmission
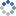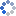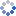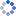
Pneumococcus frequently hides in the nasal cavity and might strike at any time when the child is weak. Bacteria can spread germs to one another by droplets and physical touch, increasing the likelihood of infection with pneumococcus and other pathogens.
Common Area
Young children and the elderly are more likely to develop invasive pneumococcal illness. Between 2007 and 2014, the local incidence rate ranged from 1.7 to 2.9 per 100,000 persons. The incidence rate is higher in children under the age of 5 and in people aged 65 or above.
If you have pneumococcal disease...
Pneumococcus is primarily transmitted through droplets produced by patients' coughing and sneezing, intimate contact with patients, or handling objects contaminated with this bacteria. Infection can cause a number of diseases, including common non-invasive diseases like otitis media, sinusitis, and pneumonia, as well as invasive diseases like meningitis, severe pneumonia, sepsis, and even death. Symptoms vary according to which part of the body is affected:
Otitis media: cause fever, ear pain, or discharge; hearing loss may occur if infection is repeated.
Pneumonia: cause fever, shortness of breath, chills, and a persistent cough; severe cases can be fatal.
Meningitis: cause fever, neck stiffness, and confusion, as well as long-term hearing loss and even death.
Bacteremia and septicemia: cause joint pain and chills, as well as infections in other sections of the body, such as pneumonia and meningitis.
Treatment
Pneumococcal infections can be treated with appropriate medicines, but the rise of drug-resistant pneumococci has made therapy more challenging.
Prevention
Vaccination against pneumococcal disease
Maintain good hygiene
Increase your immunity
13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
The 13-Valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccination is now the most effective baby pneumococcal immunization.
Hong Kong is the only area in China where people of all ages can get the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. People aged 6 weeks or older in Hong Kong can be vaccinated, however people aged 15 months or older on the Mainland cannot.
Clinical experiments have demonstrated that more than 90% of persons establish immunity following vaccination, with just minor side effects.
Guess you like